Hover over the dots to explore related posts. Closer dots are more semantically related, and the red dot marks the current page.
Abstract¶
Streamwatchr (2013–2016), developed at the University of Amsterdam, leveraged machine learning and named entity extraction to track global music listening behavior in real time through tweets. It offered features like Top-100 charts, interactive maps, and a “radio” stream mode driven by a dynamic recommender system. Using Python and MongoDB, it processed over 438 million tweets, identified 660,941 artists, and linked them to MusicBrainz and YouTube videos. This innovative blend of analytics and entity linking earned it a spot in the Dutch delegation at South by Southwest (SXSW).
Streamwatchr (2013–2016) was a web application developed at the University of Amsterdam, by Wouter Weerkamp, Maarten de Rijke, and myself. Streamwatchr monitored the Twitter feed for #nowplaying, and tracked how people interacted with songs, artists, albums, in real-time. In its latest version it also identified which parts of the lyrics were the most sung along!
Streamwatchr’s innovative approach earned it a place in the Dutch delegation for innovation at the internationally renowned South by Southwest (SXSW) festival.
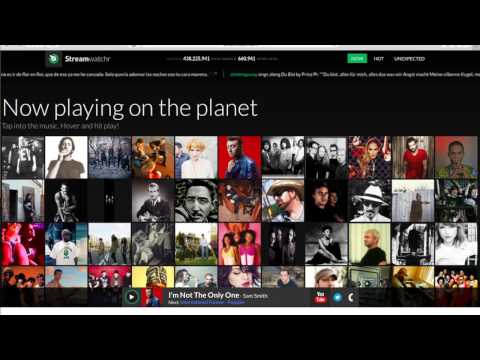
Streamwatchr provided unique insights into global music listening behavior through features such as Top-100 charts, interactive maps, and a “radio” stream mode. The radio stream played a sequence of YouTube videos, with each song following the next based on the probability of them being played together. This was achieved by linking identified songs to YouTube videos and generating playlists driven by a recommender system. Behind the scenes, the system utilized a directed graph, where nodes represented songs, and edge weights encoded the likelihood of transitioning from one song to another. These weights were dynamically updated with every incoming tweet.
The engineering behind Streamwatchr was equally groundbreaking [1]. It collected music-related tweets in real time, extracted song and artist information, and mapped them to MusicBrainz, a comprehensive music database, and corresponding YouTube video clips. Every aspect of Streamwatchr, from popularity charts and trending music to song recommendations and analytics, was refreshed with each new tweet, ensuring a dynamic and up-to-date user experience.
Streamwatchr leveraged a tech stack of Python and MongoDB for analytics and recommendations. Its real-time capabilities were powered by efficient data structures and algorithms that minimized the computational overhead required for updates, delivering a seamless and responsive experience.
The millions of tweets and the hundreds of thousands of artists that Streamwatchr has listened to over the years have been distilled to a handful of noteworthy factoids:
| Factoid | |
|---|---|
| tweets listened | 438,225,941 |
| artists seen | 660,941 |
| most popular song | Passenger – Let Her Go, 196,986 times |
| most sung along song | John Legend – All of Me, 541 times |
References¶
[1] Wouter Weerkamp, Manos Tsagkias, and Maarten de Rijke. Inside the world’s playlist. In International Conference of Knowledge Management (ICKM) 2013. ACM Library; PDF